貨號
產品規格
售價
備注
BN40721R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
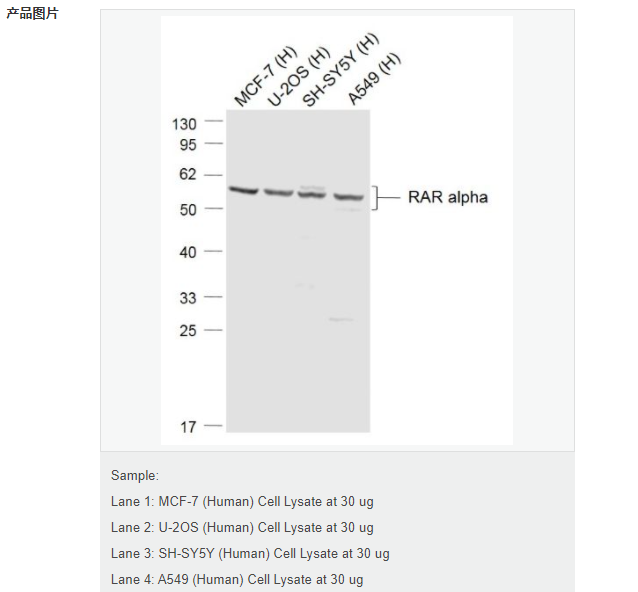
交叉反應:Human(predicted:Mouse,Rat,Chicken,Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,Sheep) 推薦應用:WB
BN40721R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反應:Human(predicted:Mouse,Rat,Chicken,Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,Sheep) 推薦應用:WB
產品描述
| 英文名稱 | RAR alpha |
| 中文名稱 | 維甲酸受體RAR α/RAR α抗體 |
| 別 名 | Acute Promelocytic Leukemia Breakpoint Cluster Region; Acute Promelocytic Leukemia Breakpoint Cluster Region; NR1B1; Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion protein; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 1; Nucleophosmin retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion protein NPM RAR long form; RAR A; RAR alpha; RAR alpha; RAR alpha form; RAR alpha form; RAR; RAR-alpha; RARA; RARA; RARA protein; RARA/PML Fusion Gene; RARA/PML Fusion Gene; RARA_HUMAN; RARalpha; RARalpha1; Retinoic acid receptor alpha; Retinoic acid receptor alpha polypeptide |
| 研究領域 | 腫瘤 細胞生物 免疫學 神經生物學 信號轉導 細胞凋亡 激酶和磷酸酶 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應 | Human, (predicted: Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Rabbit, Sheep, ) |
| 產品應用 | WB=1:500-2000 not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 51kDa |
| 細胞定位 | 細胞核 細胞漿 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human RAR alpha:161-260/462 |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產品介紹 | Acute Promelocytic Leukemia Breakpoint Cluster Region; Acute Promelocytic Leukemia Breakpoint Cluster Region; NR1B1; Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion protein; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 1; Nucleophosmin retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion protein NPM RAR long form; RAR A; RAR alpha; RAR alpha; RAR alpha form; RAR alpha form; RAR; RAR-alpha; RARA; RARA; RARA protein; RARA/PML Fusion Gene; RARA/PML Fusion Gene; RARA_HUMAN; RARalpha; RARalpha1; Retinoic acid receptor alpha; Retinoic acid receptor alpha polypeptide Function: Receptor for retinoic acid. Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RXR/RAR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. In the absence of ligand, the RXR-RAR heterodimers associate with a multiprotein complex containing transcription corepressors that induce histone acetylation, chromatin condensation and transcriptional suppression. On ligand binding, the corepressors dissociate from the receptors and associate with the coactivators leading to transcriptional activation. RARA plays an essential role in the regulation of retinoic acid-induced germ cell development during spermatogenesis. Has a role in the survival of early spermatocytes at the beginning prophase of meiosis. In Sertoli cells, may promote the survival and development of early meiotic prophase spermatocytes. In concert with RARG, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function (By similarity). Regulates expression of target genes in a ligand-dependent manner by recruiting chromatin complexes containing MLL5. Mediates retinoic acid-induced granulopoiesis. Subunit: Heterodimer; with RXRA. Binds DNA preferentially as a heterodimer. Interacts with CDK7 By similarity. Interacts with coactivators NCOA3 and NCOA6. Interacts with NCOA7; the interaction requires ligand-binding. Interacts with MLL5. Interacts (via the ligand-binding domain) with PRAME; the interaction is ligand (retinoic acid)-dependent. Interacts with AKT1; the interaction phosphorylates RARA and represses transactivation. Interacts with PRKAR1A; the interaction negatively regulates RARA transcriptional activity. Interacts with NCOR1 and NCOR2. Interacts with PRMT2. Interacts with LRIF1. Interacts with ASXL1 and NCOA1. Subcellular Location: Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Nuclear localization depends on ligand binding, phosphorylation and sumoylation. Transloaction to the nucleus in the absence of ligand is dependent on activation of PKC and the downstream MAPK phosphorylation. Post-translational modifications: Phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues. Phosphorylation does not change during cell cycle. Phosphorylation on Ser-77 is crucial for transcriptional activity. Phosphorylation by AKT1 is required for the repressor activity but has no effect on DNA binding, protein stability nor subcellular localization. Phosphorylated by PKA in vitro. This phosphorylation on Ser-219 and Ser-369 is critical for ligand binding, nuclear localization and transcriptional activity in response to FSH signaling. Sumoylated with SUMO2, mainly on Lys-399 which is also required for SENP6 binding. On all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) binding, a confromational change may occur that allows sumoylation on two additional site, Lys-166 and Lys-171. Probably desumoylated by SENP6. Sumoylation levels determine nuclear localization and regulate ATRA-mediated transcriptional activity. Trimethylation enhances heterodimerization with RXRA and positively modulates the transcriptional activation. Ubiquitinated. DISEASE: Chromosomal aberrations involving RARA are commonly found in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Translocation t(11;17)(q32;q21) with ZBTB16/PLZF; translocation t(15;17)(q21;q21) with PML; translocation t(5;17)(q32;q11) with NPM. The PML-RARA oncoprotein requires both the PML ring structure and coiled-coil domain for both interaction with UBE2I, nuclear microspeckle location and sumoylation. In addition, the coiled-coil domain functions in blocking RA-mediated transactivation and cell differentiation. Similarity: Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily. Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain. SWISS: P11416 Gene ID: 5914 Database links: Entrez Gene: 5914 Human Entrez Gene: 19401 Mouse Omim: 180240 Human SwissProt: P10276 Human SwissProt: P11416 Mouse Unigene: 654583 Human Unigene: 439744 Mouse Unigene: 91057 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. 類固醇受體(Steroid Receptors) RAR-α在人組織細胞分化過程中具有重要作用,尤其在腫瘤分化的特殊階段起到一定的作用,在造血細胞中,RARα表達豐富。 |